Have you ever wondered how Germany manages to recycle so much of its waste? Understanding the recycling system in Germany can help you see how simple actions make a big difference.
This system is designed to be easy for you to follow while protecting the environment. By learning how it works, you can discover practical tips to improve your own recycling habits. Keep reading, and you’ll find out how Germany turns everyday trash into valuable resources—and how you can do the same.
Recycling Culture In Germany
Germany’s recycling culture is one of the strongest in the world. People here take recycling seriously. It is part of everyday life. This culture grew over many years. It helps protect the environment and saves resources. Everyone plays a role in this system.
Historical Background
Germany started recycling efforts after World War II. Resources were scarce. People learned to reuse and recycle. The government introduced laws to support recycling. The Green Dot system began in the 1990s. It made packaging recycling easier and more efficient.
Public Participation
Citizens sort their waste carefully. Separate bins for paper, plastic, glass, and organic waste are common. People follow strict rules for recycling. Schools teach children about recycling from a young age. Communities organize collection days for special waste. This high participation keeps recycling rates high.
Environmental Awareness
Many Germans understand the impact of waste on nature. They want to reduce pollution and save energy. Recycling is seen as a duty to the planet. Media and campaigns raise awareness regularly. This strong environmental mindset supports recycling efforts deeply.

Credit: www.tomra.com
Key Components Of The System
The recycling system in Germany works through several key parts. These parts help collect, sort, and recycle waste efficiently. Each step plays an important role in making sure materials get reused. Understanding these components gives a clear view of how Germany keeps its environment clean.
Collection Methods
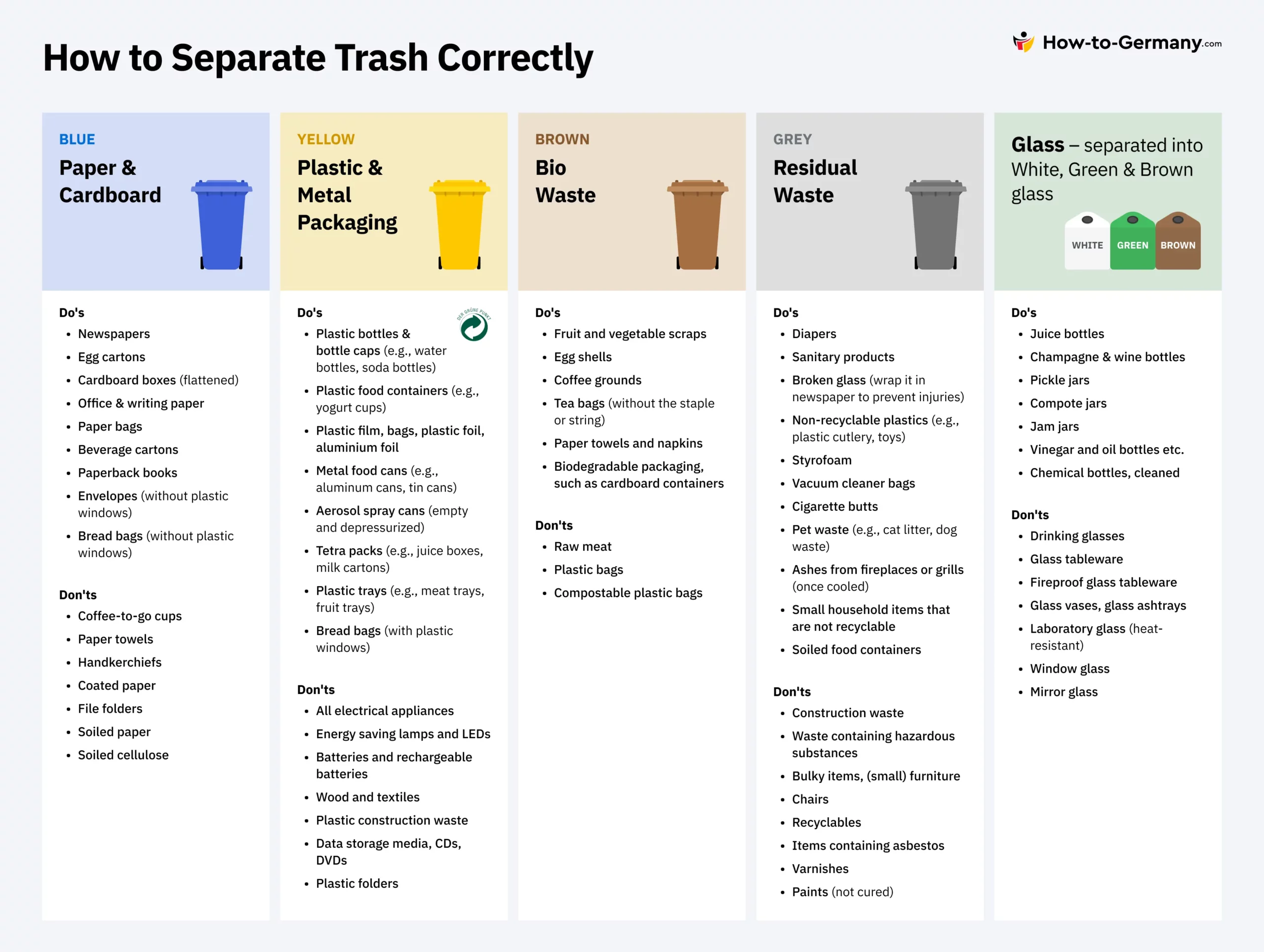
Germany uses different bins for separate waste types. Households sort waste into categories like paper, glass, plastic, and organic. Special containers are placed in public spaces for easy access. Some areas have curbside pickup, while others use drop-off points. This method makes sure waste is collected correctly from the start.
Sorting Processes
Once collected, waste goes to sorting centers. Machines and workers separate items by material type. Technology like magnets and air jets helps sort metals and plastics. Proper sorting is vital for recycling quality materials. It reduces contamination and improves recycling rates.
Recycling Facilities
Recycling plants process sorted waste into new materials. Paper is pulped and remade, glass is melted and reshaped. Plastics are cleaned and transformed into pellets for new products. These facilities turn waste into valuable resources. This step closes the loop in the recycling chain.
Packaging Waste Regulations
Germany has strict rules to manage packaging waste. These rules help reduce litter and protect the environment. The system makes sure packaging is reused or recycled properly. Everyone plays a part, from producers to consumers.
Deposit Return Schemes
Deposit return schemes encourage people to return bottles and cans. Customers pay a small deposit when buying drinks. They get their money back by returning empty containers. This system reduces waste and boosts recycling rates.
Packaging Laws
Packaging laws set clear limits on waste and pollution. They require packaging to be recyclable or reusable. Producers must follow these rules to reduce environmental harm. The laws push for less plastic and more eco-friendly materials.
Producer Responsibilities
Producers must register with waste management systems. They pay fees based on the packaging they put on the market. They also must take part in recycling programs. This shared responsibility helps keep Germany’s environment clean.
Credit: www.how-to-germany.com
Role Of Local Authorities
Local authorities play a key role in Germany’s recycling system. They organize and manage many parts of waste collection and recycling. Their efforts make recycling easy and effective for residents. Local governments also promote cleaner environments and help meet national recycling goals.
Waste Management Services
Local authorities provide waste collection services. They arrange separate bins for paper, plastic, glass, and organic waste. They schedule regular pickups to keep neighborhoods clean. Authorities also maintain recycling centers where people bring special waste. These services ensure waste is sorted properly from the start.
Community Programs
Local governments run programs to educate residents about recycling. They offer workshops, leaflets, and campaigns to spread awareness. These programs teach how to sort waste and why it matters. Community efforts encourage people to recycle more and reduce litter. Schools and local groups often join these initiatives.
Enforcement And Compliance
Local authorities enforce recycling rules strictly. They monitor waste disposal and issue fines for violations. This keeps residents responsible for sorting their waste correctly. Regular checks help prevent illegal dumping and contamination. Enforcement ensures the recycling system works smoothly and fairly for all.
Innovations Driving Success
Germany’s recycling system owes much of its success to smart innovations. These new ideas help reduce waste and improve reuse. The system keeps getting better through technology and smart planning. Understanding these innovations shows why Germany leads in recycling efforts.
These changes focus on making recycling easier and more efficient for everyone. They also help save resources and protect the environment. The future of recycling in Germany looks bright thanks to these advances.
Technological Advances
Machines now sort waste faster and more accurately than before. Advanced sensors detect different materials automatically. This speeds up recycling and lowers mistakes. New machines also break down plastics and metals better. This helps turn waste into new products more easily.
Digital Tracking Systems
Digital tools track waste from homes to recycling plants. Barcodes and RFID tags follow materials through the system. This helps identify where waste comes from and how it is handled. Tracking stops lost or mixed-up materials. It also encourages people to recycle more carefully.
Circular Economy Initiatives
Germany supports a circular economy to reduce waste. Products are designed to be reused or recycled quickly. Companies repair and reuse items instead of throwing them away. This saves raw materials and energy. Circular thinking keeps materials in use for longer.

Credit: earth.org
Challenges And Improvements
Germany’s recycling system is strong but not without problems. Challenges slow down progress and show where improvements are needed. Understanding these issues helps to see how the system can get better.
Contamination Issues
One big problem is contamination in recycling bins. People often mix wrong items with recyclables. This makes sorting harder and lowers the quality of recycled materials. Cleaning and separating these materials takes more time and money. Educating citizens to sort waste correctly is a key step to reduce contamination.
Rural Vs Urban Differences
Recycling works better in cities than in rural areas. Cities have more bins and better collection services. Rural zones face challenges like fewer collection points and longer travel distances for trucks. These factors make recycling less efficient outside cities. Improving access and service in rural areas could raise recycling rates nationwide.
Future Policy Directions
Germany plans new rules to improve recycling. Policies aim to reduce waste and increase reuse. Stricter rules on packaging and product design are expected. The government wants to support recycling technology and public awareness. These changes may help make the system cleaner and more efficient over time.
Global Impact And Lessons
The recycling system in Germany has left a mark far beyond its borders. Its success teaches important lessons about waste management and environmental care. Many countries watch closely to learn how to improve their recycling efforts.
Germany’s approach shows that clear rules and public participation matter most. Recycling is not just a local effort; it has a global impact on reducing waste and saving resources. The world benefits as more nations adopt better recycling methods.
Influence On Other Countries
Germany’s recycling system inspires many nations. Countries in Europe and beyond study its laws and practices. They see how sorting waste carefully leads to higher recycling rates. This system also lowers landfill use and cuts pollution. Governments use Germany’s model to shape their own rules.
Its success proves that organized recycling can work everywhere. Many cities copy the color-coded bins and deposit return schemes. This helps people recycle more and waste less. The system’s influence spreads through education and policy change worldwide.
Adapting The Model Worldwide
Not all countries can use Germany’s system exactly. Each nation has different needs and resources. Some adapt the model to fit local culture and economy. Others start small with simple waste sorting programs. Over time, they build stronger recycling networks.
Training and awareness campaigns help people join the effort. Technology also plays a role in improving recycling processes. Flexible approaches make the system work in various places. The goal remains the same: reduce waste and protect nature.
Sustainability Goals
Germany’s recycling system supports global sustainability targets. It helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions by cutting waste. Recycling saves energy and natural resources too. This aligns with goals to fight climate change and conserve the planet.
Countries adopting similar recycling methods contribute to a cleaner Earth. The system shows how daily actions connect to big environmental benefits. Waste management becomes a key part of sustainable living worldwide. Small steps in recycling lead to lasting positive change.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The German Recycling System?
The German recycling system is a comprehensive waste management approach. It emphasizes sorting waste into categories for efficient recycling. The system includes separate bins for paper, plastics, glass, and organic waste. It promotes environmental sustainability and reduces landfill use effectively.
How Does The Pfand System Work In Germany?
The Pfand system is a deposit return scheme for bottles and cans. Consumers pay a small deposit when buying drinks. Returning the empty containers to collection points refunds this deposit. It encourages recycling and reduces litter in public spaces.
Why Is Waste Separation Important In Germany?
Waste separation ensures recyclable materials are processed correctly. It helps reduce contamination in recycling streams. This increases recycling efficiency and conserves natural resources. Proper sorting also lowers waste disposal costs and environmental impact.
Which Materials Are Recyclable In Germany?
Common recyclable materials include paper, cardboard, plastics, glass, and metals. Organic waste is collected separately for composting. Hazardous waste has special disposal requirements. Knowing correct sorting rules helps maintain the system’s effectiveness.
Conclusion
Germany’s recycling system shows how small actions help the environment. Sorting waste correctly saves resources and reduces pollution. Everyone plays a role in keeping cities clean and green. Clear rules and easy bins make recycling simple for all. This system proves that teamwork can protect nature for future generations.
Following these steps can inspire other countries to do the same. Recycling is not just a habit, but a responsibility we share. Together, we create a healthier planet, one bin at a time.
